We all know the purpose of Jenkins but how to integrate it with a selenium project which uses Java and Maven.
Prerequisite: Install Java, Maven, and Jenkins in the system where test case execution needs to be performed.
Step 1: Install few plugin in Jenkins shown in the pic below.
Prerequisite: Install Java, Maven, and Jenkins in the system where test case execution needs to be performed.
Step 1: Install few plugin in Jenkins shown in the pic below.
Step 2: Goto "Manage Jenkins" -> "Global Tool Configuration" and configure Java and Maven. setup the path of JAVA_HOME and MAVEN_HOME as per your system configuration.
Step 3: Goto Jenkins -> New Item -> Give a name to this project like "DummyAutomation" -> Select "Freestyle project" and click OK.
Step 4: In this new DummyAutomation Project, Goto "Build" Section and click "Add Build Step" and select "Invoke top-level Maven targets".
Step 5: Select the "Maven Version", given in step 2. Set the goal "clean install" and set the path of POM file as shown in the pic below.
We are done with the basic set up of Jenkins.
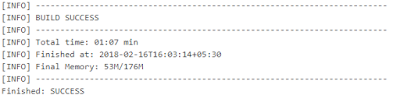
Step 6: Save the project and click on "Build Now". Project will execute with a success
There are certain other advance areas that you can touch and make your Jenkins setup more reliable
Step 7: you can setup the email notification by selection "Editable Email Notification" in "Post-build Actions".